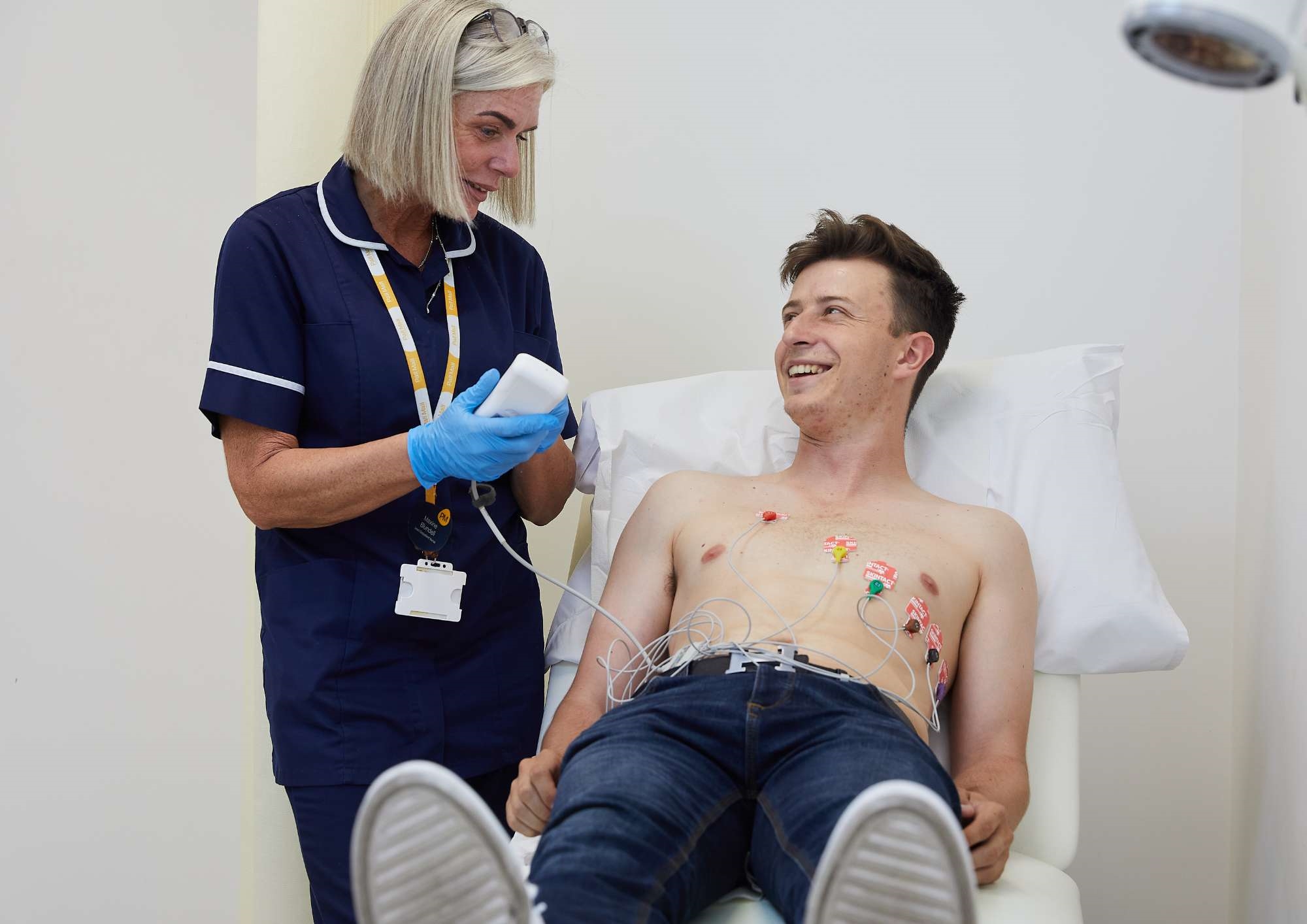
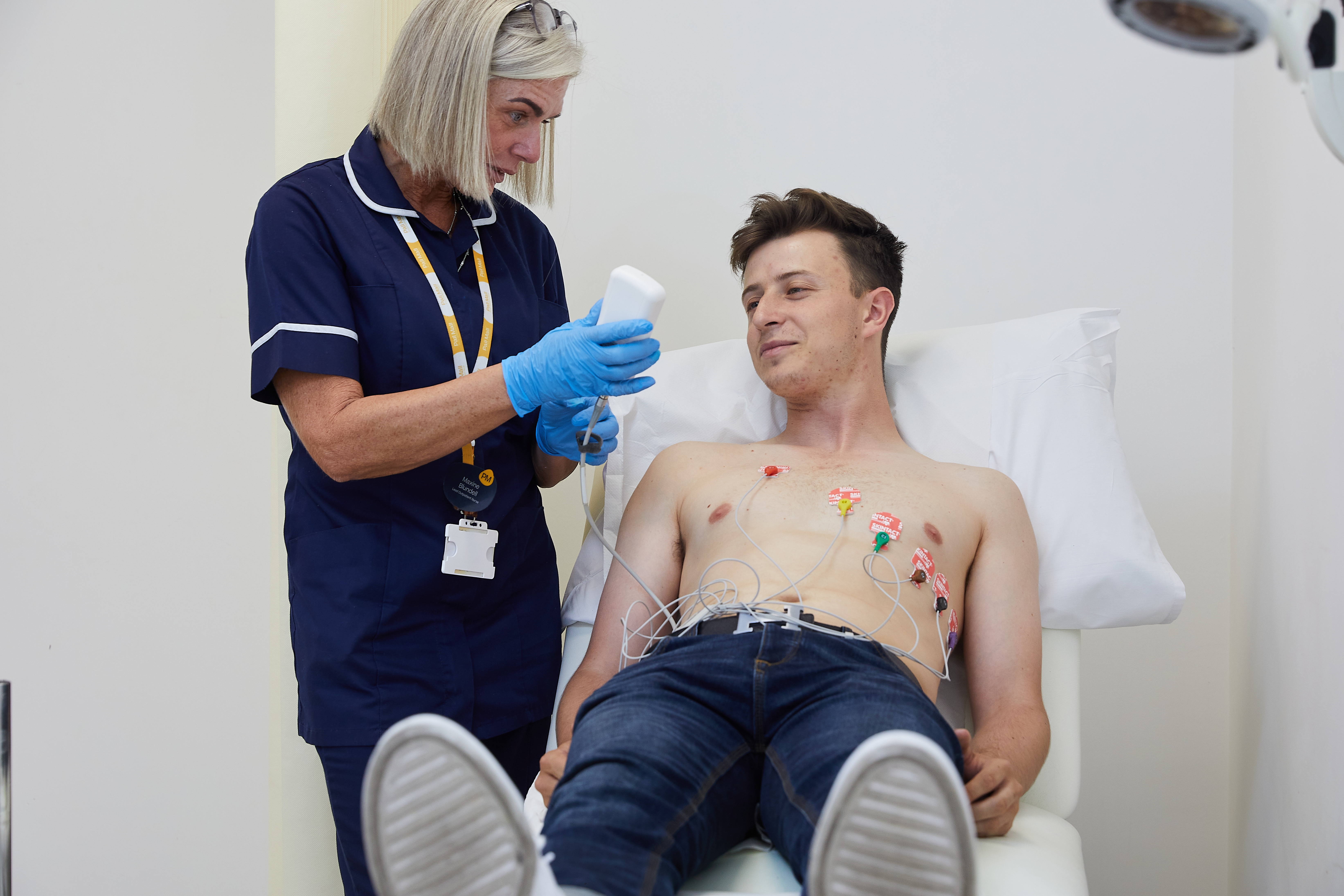
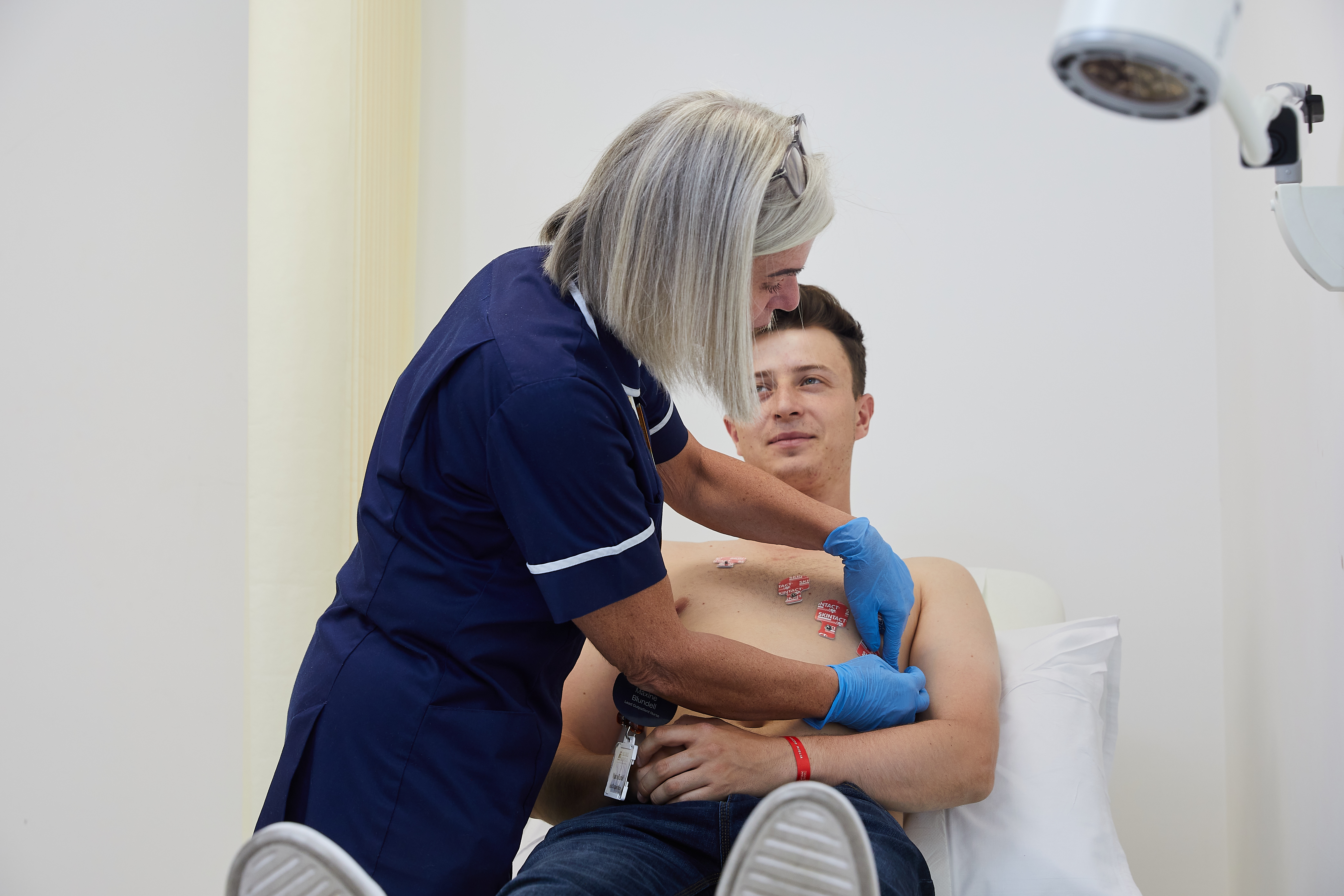
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to record the heart’s rhythm and electrical activity. The purpose of an ECG is to find out if the heart is healthy by detecting irregular heart rhythms and to help diagnose the cause of symptoms such as chest pain or palpitations.
During an ECG, the heart’s electrical activity is measured through electrodes that are attached to the skin with adhesive pads. Signals recorded from your heart are displayed on a screen and can be traced out on a piece of paper. An ECG can identify problems with your heart including:
A heart attack
An enlarged heart that is working under strain
Fast, slow or irregular heartbeats called arrhythmias
An ECG can also help investigate the cause of chest pain, palpitations, or symptoms such as difficulty in breathing. It is also used to assess if a patient has had a heart attack or to look for evidence of a previous heart attack. A standard ECG is a very simple and quick procedure that is completely painless.